Project Management
Project Management Project management is the practice of planning, executing, controlling, and closing projects to achieve specific goals and meet specific success criteria within a specified time. It involves coordinating resources, tasks, and stakeholders to complete a project successfully. key …
Overview
Project Management
Project management is the practice of planning, executing, controlling, and closing projects to achieve specific goals and meet specific success criteria within a specified time.
It involves coordinating resources, tasks, and stakeholders to complete a project successfully.
key aspects of project management:
- Project Definition: This involves defining the project’s objectives, scope, stakeholders, and constraints.
- A clear project definition is essential for setting the project’s direction.
- Project Planning: In this phase, project managers develop a comprehensive project plan, including a schedule, budget, resource allocation, risk assessment, and quality standards. Planning is critical for setting expectations and guiding the project’s execution.
- Project Execution: During this phase, the project plan is put into action.
- Project managers and team members work on their assigned tasks, and progress is monitored closely to ensure that the project stays on track.
- Monitoring and Controlling: Throughout the project’s execution, project managers must continuously monitor and control project performance.
- They compare actual progress to the plan, identify and address issues, and make necessary adjustments.
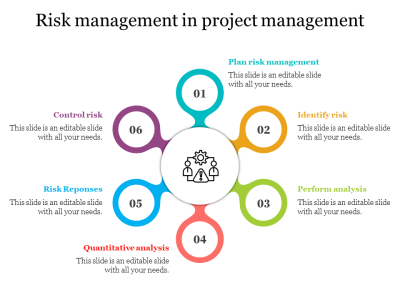
- Risk Management: Identifying and mitigating risks is a crucial part of project management.
- Project managers must anticipate potential problems and have plans in place to address them.
- Quality Management: Ensuring the quality of project deliverables is essential.
More:
- Quality standards are defined in the project plan, and project managers must ensure that these standards are met.
- Communication: Effective communication is a fundamental project management skill.
- Project managers need to keep stakeholders informed, resolve conflicts, and ensure that everyone is on the same page regarding project objectives and progress.
- Resource Management: Managing resources, including human resources, equipment, and materials, is critical. Project managers must allocate resources efficiently to meet project goals.
- Stakeholder Management: Identifying and engaging stakeholders is crucial to project success.
- Understanding their needs and expectations, and keeping them informed, can help prevent misunderstandings and conflicts.
- Project Closure: At the end of the project, there’s a formal closure phase where project managers ensure that all project objectives have been met, that all deliverables are accepted, and that the project is officially closed.
- A post-project review is often conducted to gather lessons learned.
- Project Management Methodologies: There are various methodologies used in project management, such as Agile, Waterfall, and Hybrid approaches. The choice of methodology depends on the project’s nature and requirements.
- Project Management Software: Various software tools and platforms are available to assist project managers in planning, scheduling, and tracking project progress. These tools often include features like Gantt charts, task management, and collaboration features.
Project management is a discipline that is applicable across various industries and sectors, including construction, IT, healthcare, and more.
Effective project management can lead to successful project completion, meeting deadlines, staying within budget, and delivering high-quality results.
concepts and terms related to project management:
- Scope Creep: This occurs when changes, additions, or expansions to the project scope are introduced without proper evaluation or approval.
- Scope creep can lead to project delays and increased costs.
- Critical Path: In project scheduling, the critical path is the sequence of tasks that, if delayed, will extend the project’s duration.
- Identifying and managing the critical path is essential for ensuring the project stays on track.
- Milestones: Milestones are significant events or achievements within a project that help track progress.
- They are often used to mark the completion of major project phases.
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS): The WBS is a hierarchical breakdown of a project into smaller, manageable components, making it easier to assign tasks, estimate resources, and track progress.
And:
- Project Portfolio Management (PPM): PPM involves managing a collection of projects as a portfolio, with the goal of aligning them with the organization’s strategic objectives and optimizing resource allocation.
- Agile Project Management: Agile is a flexible and iterative approach that is well-suited for projects with changing requirements.
- It emphasizes collaboration, customer feedback, and delivering incremental value.
- Scrum: A popular framework within Agile, Scrum is characterized by short, time-boxed iterations called “sprints” and emphasizes daily stand-up meetings, product backlog prioritization, and incremental development.
- Kanban: Kanban is another Agile methodology that uses visual boards to manage and control work in progress.
- It focuses on optimizing the flow of work and limiting work in progress to enhance efficiency.
- Project Management Office (PMO): A PMO is a centralized group or department within an organization responsible for defining and maintaining project management standards, practices, and methodologies.
- Earned Value Management (EVM): EVM is a technique used to measure project performance by comparing the planned work and budget to actual progress. It helps project managers assess whether a project is on track or over/under budget.
- Project Risk Management: Identifying, analyzing, and mitigating project risks is crucial. Risk management involves assessing potential threats and opportunities and having strategies in place to address them.
More:
- Change Control: A change control process is used to manage and approve changes to the project scope, schedule, or budget. This ensures that changes are evaluated, approved, and properly integrated into the project.
- Stakeholder Register: This document contains information about all project stakeholders, their interests, and their level of influence. It’s essential for effective stakeholder management.
- Project Charter: A project charter is a formal document that authorizes the project and provides a high-level overview of its purpose, objectives, and stakeholders. It is often created at the project’s initiation.
- Quality Assurance (QA) vs. Quality Control (QC): QA involves the processes and standards that ensure quality throughout the project, while QC is the process of inspecting and verifying that the project’s deliverables meet quality standards.
- Dependencies: In project management, dependencies represent the relationships between different tasks or activities, showing which tasks need to be completed before others can start.
Project management is a dynamic field, with many methodologies, tools, and best practices.
Tailoring the approach to suit the specific needs and constraints of a project is essential for success.
Curriculum
- 1 Section
- 1 Lesson
- 1 Hour